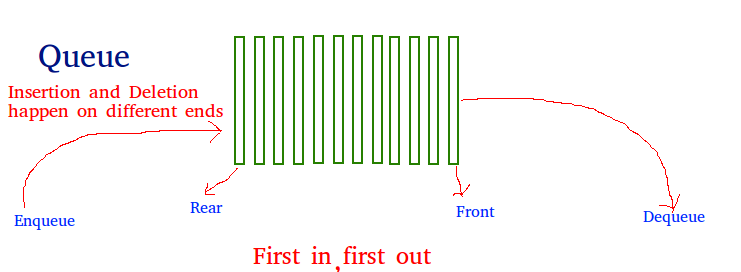
Like a stack, the queue is a linear data structure that stores items in a First In First Out (FIFO) manner. With a queue, the least recently added item is removed first. A good example of a queue is any queue of consumers for a resource where the consumer that came first is served first.

Operations associated with queue are:
There are various ways to implement a queue in Python. This article covers the implementation of queue using data structures and modules from Python library. Python Queue can be implemented by the following ways:
List is a Python's built-in data structure that can be used as a queue. Instead of enqueue() and dequeue(), append() and pop() function is used. However, lists are quite slow for this purpose because inserting or deleting an element at the beginning requires shifting all of the other elements by one, requiring O(n) time.
The code simulates a queue using a Python list. It adds elements 'a', 'b', and 'c' to the queue and then dequeues them, resulting in an empty queue at the end. The output shows the initial queue, elements dequeued ('a', 'b', 'c'), and the queue's empty state.
queue = []
queue.append('a')
queue.append('b')
queue.append('c')
print("Initial queue")
print(queue)
print("\\nElements dequeued from queue")
print(queue.pop(0))
print(queue.pop(0))
print(queue.pop(0))
print("\\nQueue after removing elements")
print(queue)
Output:
Initial queue
['a', 'b', 'c']
Elements dequeued from queue
a
b
c
Queue after removing elements
[]